Why Does Water Reflect Images
- Why Does Water Reflect Images In Science
- Why Does Water Reflect Images In Color
- Why Does Water Reflect Images In Hindi

WATER AND SOLAR REFLECTION / ABSORPTION-WATER AND SOLAR REFLECTION / ABSORPTIONMETEOROLOGIST JEFF HABYThe earth is covered with 70% water thus the amount of solar reflection and absorption has a profoundinfluence on the global temperatures. What is interesting about water is how variable the amount ofreflection and absorption is. Whether the water is liquid or solid has a significant influence. Thesun angle is a prime determinate in how much reflection and absorption take place. The concept ofreflection is explained through albedo. Albedo is how reflective a substance is. A substance with a highalbedo will reflect a high percentage of the solar radiation striking it.
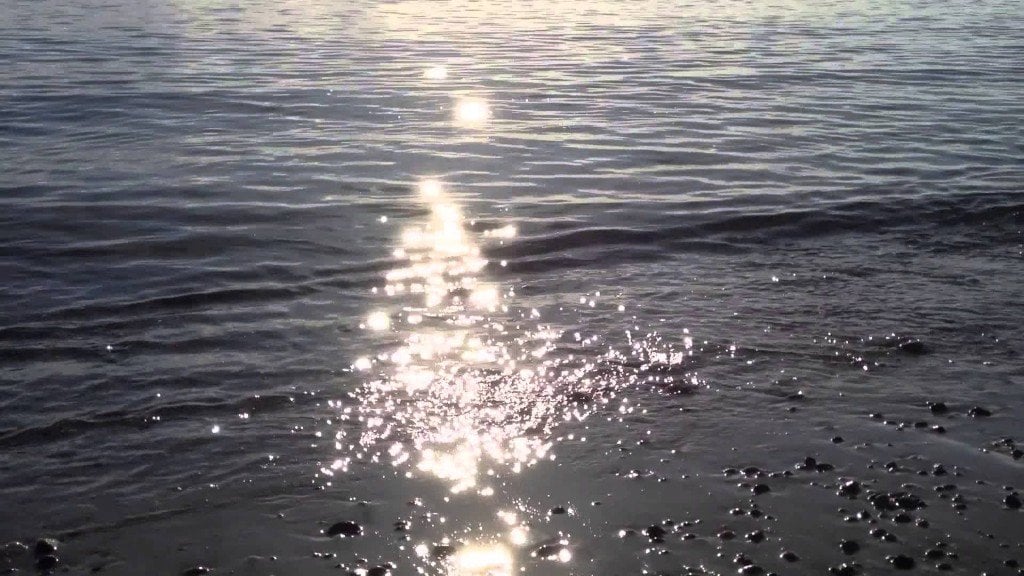
You can see that for n1 = 1 (air), and n2 = 1.33 (Water), you will get about a 2% reflection. If things are dark at the bottom of the pool, then you will be able to see your reflection by this 2% light. However, if there is lot of light coming from underneath, your reflection will appear faint, or will be totally swamped by the other light sources. Just as images are reflected from the surface of a mirror, light reflected from a smooth water surface also produced a clear image. We call the reflection from a smooth, mirror-like surface specular (as shown in Figure 2a). When the surface of water is wind-blown and irregular, the rays of light are reflected in many directions.
Why Does Water Reflect Images In Science
A 100% albedo (highestalbedo possible) would be all the solar radiation being reflected away. A 0% albedo would mean none of thesolar radiation is reflection and thus all is absorbed into or transmitted through the substance.First we will examine sun angle. When the sun is low on the horizon (low sun angle) more radiation willbe reflected off water (especially if it is ice). A low sun angle has a more difficult time warming water becausea great percentage of the solar radiation is reflected away. This dramatically changes though as the sunclimbs higher in the sky. When the sun is directly overhead the liquid water will absorb just about all thesolar radiation striking it. This adds an enormous amount of heat energy to the tropical oceans since thesun is high in the sky.
Why Does Water Reflect Images In Color
The tropical oceans not only get a denser amount of solar radiation striking it butmore of that solar radiation is absorbed as compared to polar ocean water.Next we will examine whether the water is liquid or ice. Ice acts like a mirror to incoming solar radiationwhen the sun angle is low. Less solar radiation is absorbed by ice than into water given the samesun angle. In the polar areas the sun angle is low and some of the land and ocean surface is covered in ice.This is a reason why the polar areas are cold- less density of sunlight and what does get through has agreat percentage of it reflected away.
Why Does Water Reflect Images In Hindi

The polar liquid oceans are much warmer than the ice coveredsurfaces since liquid water will absorb more solar radiation. One consequence of global warming is thatthe reduction in the ice caps results in more liquid water which in turn results in much warmertemperatures. It is the polar areas that will by far warm the most when global warming takes place sincepolar ice will be replaced by land and water.In conclusion, the state of water (liquid or ice) and the sun angle have a significant influence on theamount of reflection that takes place. More reflection takes place when the sun angle is low and when thesurface is ice while less reflection takes place when the sun angle is high and the water is liquid.
Diffuse reflection is when light hits an object and reflects in lots of different directions. This happens when the surface is rough.
Most of the things we see are because light from a source has reflected off it.For example, if you look at a bird, light has reflected off that bird and travelled in nearly all directions. If some of that light enters your eyes, it hits the retina at the back of your eyes. An electrical signal is passed to your brain, and your brain interprets the signals as an image.
Specular reflection. The angle at which light hits a reflecting surface is called the angle of incidence, and the angle at which light bounces off a reflecting surface is called the angle of reflectionIf you want to measure these angles, imagine a perfectly straight line at a right angle to the reflective surface (this imaginary line is called ‘normal’). If you measure the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection against the normal, the angle of incidence is exactly the same as the angle of reflection.
With a flat mirror, it is easy to show that the angle of reflection is the same as the angle of incidence.Water is also a reflective surface. When the water in a lake or sea is very still, the reflection of the landscape is perfect, because the reflecting surface is very flat. However, if there are ripples or waves in the water, the reflection becomes distorted. This is because the reflecting surface is no longer flat and may have humps and troughs caused by the wind.It is possible to make mirrors that behave like humps or troughs, and because of the different way they reflect light, they can be very useful. Concave mirrors.
The inside curve of a spoon is an example of a concave mirrorConcave mirrors are used in certain types of astronomical telescopes called reflecting telescopes. The mirrors condense lots of light from faint sources in space onto a much smaller viewing area and allow the viewer to see far away objects and events in space that would be invisible to the naked eye.Light rays travel towards the mirror in a straight line and are reflected inwards to meet at a point called the focal point.Concave mirrors are useful for make-up mirrors because they can make things seem larger. This concave shape is also useful for car headlights and satellite dishes. Convex mirrors. Convex mirrors curve outwards, like the outside of a balloon.Parallel rays of light strike the mirror and are reflected outwards. If imaginary lines are traced back, they appear to come from a focal point behind the mirror.Convex mirrors are useful for shop security and rear-view mirrors on vehicles because they give a wider field of vision. Scattering of lightSome light is scattered in all directions when it hits very small particles such as gas molecules or much larger particles such as dust or droplets of water.The amount of scattering depends on how big the particle is compared to the wavelength of light that is hitting it.
Smaller wavelengths are scattered more.“Why is the sky blue?” is a common question. Light from the sun is made of all the colours of the rainbow. As this light hits the particles of nitrogen and oxygen in our atmosphere, it is scattered in all directions. Blue light has a smaller wavelength than red light, so it is scattered much more than red light. When we look at the sky, we see all the places that the blue light has been scattered from.This is similar to the question: “Why are sunsets red?” When the Sun appears lower in the sky, the light that reaches us has already travelled through a lot more of the atmosphere. This means that a lot of the blue light has been scattered out well before the light arrives at us, so the sky appears redder.Clouds appear white because the water droplets are much larger than the wavelengths of light.
For this situation, all wavelengths of light are equally scattered in all directions.